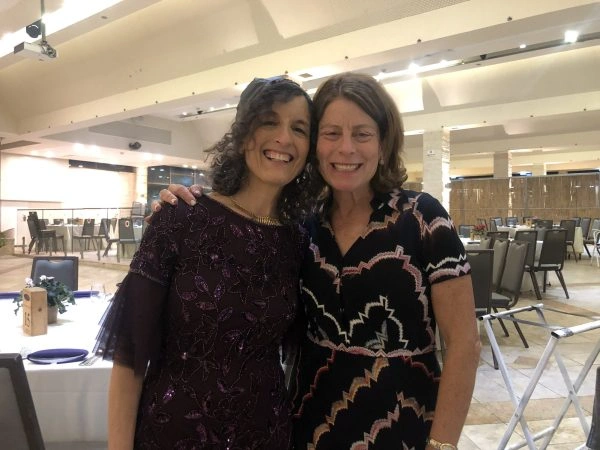
The court excommunicates those who mock the rabbis or don’t listen to the words of the rabbis. According to Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi, this is found 24 times in the mishna. The gemara tries to figure out where are these 24 occurences. the gemara delves into the issues regarding the exemptions of those attending the burial and making up the rows for the mourners. In what situations are the exempt or not exempt? Does human dignity override Torah or rabbinic law?
Berakhot 19
Share this shiur:
Want to dedicate learning? Get started here:
New to Talmud?
Check out our resources designed to help you navigate a page of Talmud – and study at the pace, level and style that fits you.
The Hadran Women’s Tapestry
Meet the diverse women learning Gemara at Hadran and hear their stories.
Berakhot 19
וְאִי סָלְקָא דַעְתָּךְ דְּלָא יָדְעִי, כִּי אָמַר לְהוּ מַאי הָוֵי? אֶלָּא מַאי — דְּיָדְעִי? לְמָה לֵיהּ לְמֵימַר לְהוּ?! לְאַחְזוֹקֵי לֵיהּ טֵיבוּתָא לְמֹשֶׁה.
And if it should enter your mind that the dead do not know, then what of it if he tells them? The Gemara rejects this: Rather what will you say, that they know? Then why does he need to tell them? The Gemara replies: This is not difficult, as he is telling them so that they will give credit to Moses.
אָמַר רַבִּי יִצְחָק: כׇּל הַמְסַפֵּר אַחֲרֵי הַמֵּת, כְּאִלּוּ מְסַפֵּר אַחֲרֵי הָאֶבֶן. אִיכָּא דְאָמְרִי דְּלָא יָדְעִי, וְאִיכָּא דְאָמְרִי דְּיָדְעִי וְלָא אִיכְפַּת לְהוּ.
On this subject, Rabbi Yitzḥak said: Anyone who speaks negatively after the deceased it is as if he speaks after the stone. The Gemara offers two interpretations of this: Some say this is because the dead do not know, and some say that they know, but they do not care that they are spoken of in such a manner.
אִינִי?! וְהָא אָמַר רַב פָּפָּא: חַד אִישְׁתַּעִי מִילְּתָא בָּתְרֵיהּ דְּמָר שְׁמוּאֵל וּנְפַל קַנְיָא מִטְּלָלָא וּבְזַעָא לְאַרְנְקָא דְמוֹחֵיהּ!
The Gemara asks: Is that so? Didn’t Rav Pappa say: There was once someone who spoke disparagingly after the death of Mar Shmuel and a reed fell from the ceiling, fracturing his skull? Obviously, the dead care when people speak ill of them.
שָׁאנֵי צוֹרְבָא מֵרַבָּנָן, דְּקוּדְשָׁא בְּרִיךְ הוּא תָּבַע בִּיקָרֵיהּ.
The Gemara rejects this: This is no proof that the dead care. Rather, a Torah scholar is different, as God Himself demands that his honor be upheld.
אָמַר רַבִּי יְהוֹשֻׁעַ בֶּן לֵוִי: כׇּל הַמְסַפֵּר אַחַר מִטָּתָן שֶׁל תַּלְמִידֵי חֲכָמִים נוֹפֵל בְּגֵיהִנָּם, שֶׁנֶּאֱמַר: ״וְהַמַּטִּים עֲקַלְקַלּוֹתָם יוֹלִיכֵם ה׳ אֶת פּוֹעֲלֵי הָאָוֶן שָׁלוֹם עַל יִשְׂרָאֵל״. אֲפִילּוּ בְּשָׁעָה שֶׁשָּׁלוֹם עַל יִשְׂרָאֵל, ״יוֹלִיכֵם ה׳ אֶת פּוֹעֲלֵי הָאָוֶן״.
Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi said similarly: One who speaks disparagingly after the biers of Torah scholars and maligns them after their death will fall in Gehenna, as it is stated: “But those who turn aside unto their crooked ways, the Lord will lead them away with the workers of iniquity; peace be upon Israel” (Psalms 125:5). Even if he speaks ill of them when there is peace upon Israel, after death, when they are no longer able to fight those denouncing them (Tosafot); nevertheless the Lord will lead them away with the workers of iniquity, to Gehenna.
תָּנָא דְּבֵי רַבִּי יִשְׁמָעֵאל: אִם רָאִיתָ תַּלְמִיד חָכָם שֶׁעָבַר עֲבֵירָה בַּלַּיְלָה — אַל תְּהַרְהֵר אַחֲרָיו בַּיּוֹם, שֶׁמָּא עָשָׂה תְּשׁוּבָה. ״שֶׁמָּא״ סָלְקָא דַעְתָּךְ? אֶלָּא וַדַּאי עָשָׂה תְּשׁוּבָה. וְהָנֵי מִילֵּי — בִּדְבָרִים שֶׁבְּגוּפוֹ. אֲבָל בְּמָמוֹנָא — עַד דְּמַהְדַּר לְמָרֵיהּ.
On a similar note, it was taught in the school of Rabbi Yishmael: If you saw a Torah scholar transgress a prohibition at night, do not think badly of him during the day; perhaps he has repented in the meantime. The Gemara challenges this: Does it enter your mind that only perhaps he has repented? Shouldn’t he be given the benefit of the doubt? Rather, he has certainly repented. The Gemara notes: The idea that one must always give a Torah scholar the benefit of the doubt and assume that he has repented refers specifically to matters affecting himself, but, if one witnesses a Torah scholar committing a transgression involving the property of another, one is not required to give him the benefit of the doubt. Rather, he should not assume that he has repented until he sees him return the money to its owner.
וְאָמַר רַבִּי יְהוֹשֻׁעַ בֶּן לֵוִי: בְּעֶשְׂרִים וְאַרְבָּעָה מְקוֹמוֹת בֵּית דִּין מְנַדִּין עַל כְּבוֹד הָרַב, וְכוּלָּן שָׁנִינוּ בְּמִשְׁנָתֵנוּ. אֲמַר לֵיהּ רַבִּי אֶלְעָזָר: הֵיכָא? אֲמַר לֵיהּ: לְכִי תַּשְׁכַּח.
Since matters relating to the respect due Torah scholars were raised, the Gemara continues, citing Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi, who said: There are twenty-four places in which the court ostracizes over matters of respect due the rabbi, and we learned them all in our Mishna. Rabbi Elazar said to him: Where are those cases to be found? Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi said to him: When you look, you will find them.
נְפַק דָּק, וְאַשְׁכַּח תְּלָת: הַמְזַלְזֵל בִּנְטִילַת יָדַיִם, וְהַמְסַפֵּר אַחַר מִטָּתָן שֶׁל תַּלְמִידֵי חֲכָמִים, וְהַמֵּגִיס דַּעְתּוֹ כְּלַפֵּי מַעְלָה.
He went out, analyzed, and found three examples: One who demeans the ritual of washing of the hands, one who speaks disparagingly after the bier of Torah scholars, and one who is arrogant vis-à-vis Heaven. The Gemara cites sources for each of these cases.
״הַמְסַפֵּר אַחַר מִטָּתָן שֶׁל תַּלְמִידֵי חֲכָמִים״ מַאי הִיא? — דִּתְנַן: הוּא הָיָה אוֹמֵר: אֵין מַשְׁקִין לֹא אֶת הַגִּיּוֹרֶת, וְלֹא אֶת הַמְשׁוּחְרֶרֶת. וַחֲכָמִים אוֹמְרִים: מַשְׁקִין. וְאָמְרוּ לוֹ: מַעֲשֶׂה בְּכַרְכְּמִית, שִׁפְחָה מְשׁוּחְרֶרֶת בִּירוּשָׁלַיִם וְהִשְׁקוּהָ שְׁמַעְיָה וְאַבְטַלְיוֹן! וְאָמַר לָהֶם: דּוּגְמָא הִשְׁקוּהָ — וְנִדּוּהוּ וּמֵת בְּנִדּוּיוֹ, וְסָקְלוּ בֵּית דִּין אֶת אֲרוֹנוֹ.
What is the source for one who speaks disparagingly after the biers of Torah scholars? As we learned in the mishna: Akavya ben Mahalalel would say: In the case of a woman whose husband suspects her of adultery, who was warned by her husband not to seclude herself with another man and she did not listen (see Numbers 5), the court does not administer the bitter water potion of a sota to a convert or an emancipated maidservant. And the Rabbis say: The court administers the bitter water potion to them. And the Rabbis said to him as proof: There is the story of Kharkemit, an emancipated maidservant in Jerusalem, and Shemaya and Avtalyon administered her the bitter waters. Akavya ben Mahalalel said to the Sages: That is no proof. Shemaya and Avtalyon, who were also from families of converts, required the maidservant to drink the potion because she was like them [dugma]. And since Akavya ben Mahalalel cast aspersion on the deceased Torah scholars, he was ostracized and died while he was still under the ban of ostracism. And in accordance with the halakha with regard to one who dies while under a ban of ostracism, the court stoned his coffin. Apparently, one who deprecates a deceased Torah scholar is sentenced to ostracism.
״וְהַמְזַלְזֵל בִּנְטִילַת יָדַיִם״ מַאי הִיא? — דִּתְנַן, אָמַר רַבִּי יְהוּדָה: חַס וְשָׁלוֹם שֶׁעֲקַבְיָא בֶּן מַהֲלַלְאֵל נִתְנַדָּה, שֶׁאֵין עֲזָרָה נִנְעֶלֶת עַל כׇּל אָדָם בְּיִשְׂרָאֵל בְּחׇכְמָה וּבְטׇהֳרָה וּבְיִרְאַת חֵטְא כַּעֲקַבְיָא בֶּן מַהֲלַלְאֵל. אֶלָּא אֶת מִי נִדּוּ? — אֶת אֶלְעָזָר בֶּן חֲנוֹךְ שֶׁפִּקְפֵּק בִּנְטִילַת יָדַיִם. וּכְשֶׁמֵּת, שָׁלְחוּ בֵּית דִּין וְהִנִּיחוּ אֶבֶן גְּדוֹלָה עַל אֲרוֹנוֹ, לְלַמֶּדְךָ שֶׁכָּל הַמִּתְנַדֶּה וּמֵת בְּנִדּוּיוֹ — בֵּית דִּין סוֹקְלִין אֶת אֲרוֹנוֹ.
And what is the source for one who demeans the ritual of washing of the hands? We learned later in the same mishna: Rabbi Yehuda said: That story related with regard to the ostracism of Akavya ben Mahalalel is completely untrue; God forbid that Akavya ben Mahalalel was ostracized, as the Temple courtyard is not closed on any Jew, meaning that even when all of Israel made the pilgrimage to Jerusalem, when each of the three groups that gathered to offer the Paschal lamb filled the courtyard, leading the Temple administration to close the courtyard, there was no one there as perfect in wisdom, purity and fear of sin as Akavya ben Mahalalel. Rather, whom did they excommunicate? Elazar ben Ḥanokh, because he doubted and demeaned the rabbinic ordinance of washing of the hands. And when he died, the court sent instructions and they placed a large rock upon his coffin in order to teach you that one who is ostracized and dies in a state of ostracism, the court stones his coffin, as if symbolically stoning him. Apparently, one who makes light of the ritual of washing of the hands is sentenced to ostracism.
״הַמֵּגִיס דַּעְתּוֹ כְּלַפֵּי מַעְלָה״ מַאי הִיא? — דִּתְנַן, שָׁלַח לוֹ שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן שֶׁטַח לְחוֹנִי הַמְעַגֵּל: צָרִיךְ אַתָּה לְהִתְנַדּוֹת, וְאִלְמָלֵא חוֹנִי אַתָּה גּוֹזְרַנִי עָלֶיךָ נִדּוּי, אֲבָל מָה אֶעֱשֶׂה שֶׁאַתָּה מִתְחַטֵּא לִפְנֵי הַמָּקוֹם וְעוֹשֶׂה לְךָ רְצוֹנְךָ, כְּבֵן שֶׁמִּתְחַטֵּא לִפְנֵי אָבִיו וְעוֹשֶׂה לוֹ רְצוֹנוֹ. וְעָלֶיךָ הַכָּתוּב אוֹמֵר: ״יִשְׂמַח אָבִיךָ וְאִמֶּךָ וְתָגֵל יוֹלַדְתֶּךָ״.
What is the source for the third case, one who is arrogant vis-à-vis Heaven? The mishna relates that Ḥoni HaMe’aggel, the circle-drawer, drew a circle and stood inside it, and said that he would not leave the circle until it rained, and he went so far as to make demands in terms of the manner in which he wanted the rain to fall. After it rained, Shimon ben Shataḥ, the Nasi of the Sanhedrin, relayed to Ḥoni HaMe’aggel: Actually, you should be ostracized for what you said, and if you were not Ḥoni, I would have decreed ostracism upon you, but what can I do? You nag God and He does your bidding, like a son who nags his father and his father does his bidding without reprimand. After all, the rain fell as you requested. About you, the verse states: “Your father and mother will be glad and she who bore you will rejoice” (Proverbs 23:25). Apparently, one who is arrogant vis-à-vis Heaven would ordinarily merit excommunication.
וְתוּ לֵיכָּא? וְהָא אִיכָּא דְּתָנֵי רַב יוֹסֵף: תּוֹדוֹס אִישׁ רוֹמִי הִנְהִיג אֶת בְּנֵי רוֹמִי לְהַאֲכִילָן גְּדָיִים מְקוּלָּסִין בְּלֵילֵי פְּסָחִים. שְׁלַח לֵיהּ שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן שָׁטַח: אִלְמָלֵא תּוֹדוֹס אַתָּה, גּוֹזְרַנִי עָלֶיךָ נִדּוּי, שֶׁאַתָּה מַאֲכִיל אֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל קׇדָשִׁים בַּחוּץ.
The Gemara challenges this: And are there no more cases of excommunication or threats of excommunication? Surely there are additional cases like the one in the baraita taught by Rav Yosef: It is told that Theodosius of Rome, leader of the Jewish community there, instituted the custom for the Roman Jews to eat whole kids, young goats roasted with their entrails over their heads, as was the custom when roasting the Paschal lamb, on the eve of Passover, as they did in the Temple. Shimon ben Shataḥ sent a message to him: If you were not Theodosius, an important person, I would have decreed ostracism upon you, as it appears as if you are feeding Israel consecrated food, which may only be eaten in and around the Temple itself, outside the Temple.
״בְּמִשְׁנָתֵנוּ״ קָאָמְרִינַן. וְהָא, בָּרַיְיתָא הִיא.
The Gemara responds: This case should not be included, as Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi said that there were twenty-four cases in our Mishna, and this is merely a baraita.
וּבְמַתְנִיתִין לֵיכָּא? וְהָא אִיכָּא הָא דִתְנַן: חֲתָכוֹ חוּלְיוֹת וְנָתַן חוֹל בֵּין חוּלְיָא לְחוּלְיָא — רַבִּי אֱלִיעֶזֶר מְטַהֵר, וַחֲכָמִים מְטַמְּאִים. וְזֶהוּ תַּנּוּרוֹ שֶׁל עַכְנַאי.
The Gemara asks: And are there none in the Mishna? Isn’t there that which we learned in the mishna: One who cut an earthenware oven horizontally into ring-shaped pieces and put sand between the pieces, Rabbi Eliezer deems the oven ritually pure, i.e., it is no longer susceptible to ritual impurity. He holds that, although the fragments of the oven were pieced together, it is not considered an intact vessel but, rather, as a collection of fragments, and a broken earthenware vessel cannot become ritually impure. And the Rabbis deem it ritually impure. Since the oven continues to serve its original function, it is still considered a single entity and a whole vessel despite the sand put between the pieces. And this is called the oven of akhnai, snake.
מַאי ״עַכְנַאי״? אָמַר רַב יְהוּדָה אָמַר שְׁמוּאֵל: מְלַמֵּד שֶׁהִקִּיפוּהוּ הֲלָכוֹת כְּעַכְנַאי זֶה, וְטִמְּאוּהוּ.
The Gemara asks: What is the meaning of oven of the snake? Rav Yehuda said that Shmuel said: It is called snake to teach that the Rabbis surrounded Rabbi Eliezer with halakhot and proofs like a snake surrounds its prey, and declared the oven and its contents ritually impure.
וְתַנְיָא: אוֹתוֹ הַיּוֹם הֵבִיאוּ כׇּל טְהָרוֹת שֶׁטִּיהֵר רַבִּי אֱלִיעֶזֶר וּשְׂרָפוּם לְפָנָיו, וּלְבַסּוֹף בֵּרְכוּהוּ.
And it was taught in a baraita: On that day, they gathered all of the ritually pure food items that had come into contact with the oven that Rabbi Eliezer had declared ritually pure, and burned them before him, and because he did not accept the decision of the majority, in the end they “blessed,” a euphemism for ostracized, him. This is another case that ended in ostracism.
אֲפִילּוּ הָכִי, נִדּוּי בְּמַתְנִיתִין לָא תְּנַן. אֶלָּא ״בְּעֶשְׂרִים וְאַרְבָּעָה מְקוֹמוֹת״ הֵיכָא מַשְׁכַּחַתְּ לַהּ? רַבִּי יְהוֹשֻׁעַ בֶּן לֵוִי מְדַמֵּה מִילְּתָא לְמִילְּתָא, וְרַבִּי אֶלְעָזָר לָא מְדַמֵּה מִילְּתָא לְמִילְּתָא.
The Gemara answers: Even so, we did not learn the ruling with regard to his ostracism in the mishna. The Gemara asks: Then where do you find the twenty-four places mentioned in Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi’s statement? The Gemara responds: Rabbi Yehoshua ben Levi likens one matter to another similar matter. Whenever he would encounter a case in a mishna where one of the Sages expressed himself inappropriately in reference to other Sages, he concluded that they should have been excommunicated. Rabbi Elazar does not liken one matter to another similar matter, and therefore located only three explicit cases of ostracism.
נוֹשְׂאֵי הַמִּטָּה וְחִלּוּפֵיהֶן. תָּנוּ רַבָּנַן אֵין מוֹצִיאִין אֶת הַמֵּת סָמוּךְ לִקְרִיאַת שְׁמַע. וְאִם הִתְחִילוּ — אֵין מַפְסִיקִין. אִינִי?! וְהָא רַב יוֹסֵף אַפְּקוּהוּ סָמוּךְ לִקְרִיאַת שְׁמַע! אָדָם חָשׁוּב שָׁאנֵי.
We learned in the mishna that the pallbearers and their replacements are exempt from the recitation of Shema. On this subject, the Gemara cites that which the Sages taught in a baraita: The deceased may not be taken out to be buried adjacent to the time for the recitation of Shema, but should be buried later. And if they already started to take him out, they need not stop in order to recite Shema. The Gemara challenges: Is that so? Didn’t they take Rav Yosef out to be buried adjacent to the time for the recitation of Shema? The Gemara resolves this contradiction: The case of an important person is different, and they are more lenient in order to honor him at his burial.
שֶׁלִּפְנֵי הַמִּטָּה וְשֶׁלְּאַחַר הַמִּטָּה. תָּנוּ רַבָּנַן: הָעוֹסְקִים בְּהֶסְפֵּד, בִּזְמַן שֶׁהַמֵּת מוּטָל לִפְנֵיהֶם נִשְׁמָטִין אֶחָד אֶחָד וְקוֹרִין. אֵין הַמֵּת מוּטָל לִפְנֵיהֶם, הֵן יוֹשְׁבִין וְקוֹרִין, וְהוּא יוֹשֵׁב וְדוֹמֵם. הֵם עוֹמְדִים וּמִתְפַּלְּלִין, וְהוּא עוֹמֵד וּמַצְדִּיק עָלָיו אֶת הַדִּין, וְאוֹמֵר: ״רִבּוֹן הָעוֹלָמִים, הַרְבֵּה חָטָאתִי לְפָנֶיךָ, וְלֹא נִפְרַעְתָּ מִמֶּנִּי אֶחָד מִנִּי אֶלֶף, יְהִי רָצוֹן מִלְּפָנֶיךָ ה׳ אֱלֹהֵינוּ, שֶׁתִּגְדּוֹר פִּרְצוֹתֵינוּ וּפִרְצוֹת כׇּל עַמְּךָ בֵּית יִשְׂרָאֵל בְּרַחֲמִים״.
In the mishna, we learned the halakha with regard to the pallbearers and their obligation to recite Shema, and a distinction was made between those who are before the bier and those after the bier. Our Rabbis taught in a baraita: Those involved in eulogy must slip away from the eulogy one by one while the deceased is laid out before them and recite Shema elsewhere. And if the deceased is not laid out before them, the eulogizers must sit and recite Shema while the bereaved sits silently. They stand and pray and he stands and justifies God’s judgment, saying: Master of the Universe, I have sinned greatly against You, and You have not collected even one one-thousandth of my debt. May it be Your will, Lord our God, to mercifully repair the breaches in our fence and the breaches of Your nation, the House of Israel.
אָמַר אַבָּיֵי: לָא מִבְּעֵי לֵיהּ לְאִינָשׁ לְמֵימַר הָכִי, דְּאָמַר רַבִּי שִׁמְעוֹן בֶּן לָקִישׁ, וְכֵן תָּנָא מִשְּׁמֵיהּ דְּרַבִּי יוֹסֵי: לְעוֹלָם אַל יִפְתַּח אָדָם פִּיו לַשָּׂטָן.
Abaye said: A person should not say that, as Rabbi Shimon ben Lakish said, and it was also taught in the name of Rabbi Yosei: One must never open his mouth to the Satan, i.e., one must not leave room for or raise the possibility of disaster or evil. This formula, which states that the entire debt owed due to his transgressions has not been collected, raises the possibility that further payment will be exacted from him.
וְאָמַר רַב יוֹסֵף: מַאי קְרָאָה — שֶׁנֶּאֱמַר: ״כִּמְעַט כִּסְדוֹם הָיִינוּ״, מַאי אַהֲדַר לְהוּ נָבִיא — ״שִׁמְעוּ דְבַר ה׳ קְצִינֵי סְדוֹם״.
And Rav Yosef said: What is the verse from which it is derived? As it is stated: “We should have almost been as Sodom, we should have been like unto Gomorrah” (Isaiah 1:9), after which what did the prophet reply to them? “Hear the word of the Lord, rulers of Sodom; give ear unto the law of our God, people of Gomorrah” (Isaiah 1:10).
קָבְרוּ אֶת הַמֵּת וְחָזְרוּ וְכוּ׳. אִם יְכוֹלִים לְהַתְחִיל וְלִגְמוֹר אֶת כּוּלָּהּ אִין, אֲבָל פֶּרֶק אֶחָד אוֹ פָּסוּק אֶחָד — לָא. וּרְמִינְהוּ: קָבְרוּ אֶת הַמֵּת וְחָזְרוּ, אִם יְכוֹלִין לְהַתְחִיל וְלִגְמוֹר אֲפִילּוּ פֶּרֶק אֶחָד אוֹ פָּסוּק אֶחָד!
We learned in the mishna that, in a case when they buried the deceased and returned, if they have sufficient time to begin to recite Shema and conclude before they arrive at the row formed by those who came to console the bereaved, they should begin. Here, the Gemara clarifies: This is the case only if they can begin and complete recitation of Shema in its entirety. However, if they can only complete one chapter or one verse, they should not stop to do so. The Gemara raises a contradiction from that which we learned in the baraita: After they buried the deceased and returned, if they can begin the recitation of Shema and finish even a single chapter or verse, they should begin.
הָכִי נָמֵי קָאָמַר: אִם יְכוֹלִין לְהַתְחִיל וְלִגְמוֹר אֲפִילּוּ פֶּרֶק אֶחָד אוֹ אֲפִילּוּ פָּסוּק אֶחָד עַד שֶׁלֹּא יַגִּיעוּ לַשּׁוּרָה — יַתְחִילוּ, וְאִם לָאו — לֹא יַתְחִילוּ.
The Gemara responds: That is also what the tanna of the mishna said and this is the conclusion drawn from his statement: If one can begin and conclude even one chapter or one verse before they arrive at the row of consolers, they should begin. And if not, they should not begin.
הָעוֹמְדִים בַּשּׁוּרָה וְכוּ׳. תָּנוּ רַבָּנַן: שׁוּרָה הָרוֹאָה פְּנִימָה — פְּטוּרָה, וְשֶׁאֵינָהּ רוֹאָה פְּנִימָה — חַיֶּיבֶת. רַבִּי יְהוּדָה אוֹמֵר: הַבָּאִים מֵחֲמַת הָאָבֵל — פְּטוּרִין, מֵחֲמַת עַצְמָן — חַיָּיבִין.
We learned in the mishna that those standing in the row, those in the interior row, are exempt from reciting Shema and the others are obligated. The Sages taught this more expansively in the Tosefta: The consolers standing in a row from which one sees inside the area where the mourners are passing are exempt, and those standing in a row from which one does not see inside are obligated. And Rabbi Yehuda elaborates and says: The consolers standing in the row who come on account of the bereaved are exempt, while those who come on account of their own curiosity are obligated to recite Shema.
אָמַר רַב יְהוּדָה אָמַר רַב: הַמּוֹצֵא כִּלְאַיִם בְּבִגְדוֹ — פּוֹשְׁטָן אֲפִילּוּ בַּשּׁוּק. מַאי טַעְמָא: ״אֵין חׇכְמָה וְאֵין תְּבוּנָה וְאֵין עֵצָה לְנֶגֶד ה׳״, כׇּל מָקוֹם שֶׁיֵּשׁ חִלּוּל הַשֵּׁם אֵין חוֹלְקִין כָּבוֹד לָרַב.
We learned that some who come to console the bereaved are exempt from Shema as a means of honoring the deceased. The Gemara expands the discussion to raise the general question: To what degree does preserving human dignity take precedence over mitzvot enumerated in the Torah? Rav Yehuda said that Rav said: One who discovers diverse kinds [kilayim], i.e., a prohibited mixture of wool and linen, in his garment, must remove them even in the public marketplace. He may not wait until he reaches home. What is the reason for this? As it is stated: “There is neither wisdom, nor understanding, nor counsel against the Lord” (Proverbs 21:30). From here, the general principle: Anywhere that there is desecration of the Lord’s name, one does not show respect to the teacher, is derived.
מֵתִיבִי: קָבְרוּ אֶת הַמֵּת וְחָזְרוּ, וְלִפְנֵיהֶם שְׁתֵּי דְרָכִים, אַחַת טְהוֹרָה וְאַחַת טְמֵאָה, בָּא בַּטְּהוֹרָה — בָּאִין עִמּוֹ בַּטְּהוֹרָה, בָּא בַּטְּמֵאָה — בָּאִין עִמּוֹ בַּטְּמֵאָה מִשּׁוּם כְּבוֹדוֹ. אַמַּאי? לֵימָא ״אֵין חׇכְמָה וְאֵין תְּבוּנָה לְנֶגֶד ה׳״!
The Gemara cites several sources to challenge this principle. The Gemara raised an objection from a baraita: After they buried the deceased and returned, and on their way there are two paths before them, one ritually pure and one ritually impure, e.g., it passes through a cemetery, if the mourner comes on the pure path, they come with him on the pure path; if he comes on the impure path, all of the funeral participants accompany him on the impure path in order to show him respect. Why would they do this? Let us say here too that, “There is neither wisdom, nor understanding…against the Lord!”
תַּרְגְּמַהּ רַבִּי אַבָּא בְּבֵית הַפְּרָס דְּרַבָּנַן.
Rabbi Abba explained that the baraita is referring to a path that passes through an area where there is uncertainty with regard to the location of a grave or a corpse [beit haperas]. For example, with regard to a field in which there is a grave that was plowed and no longer intact, the entire field is deemed impure due to concern that the plow scattered bones throughout the field. The field is impure only by rabbinic law but not according to Torah law. Since it is only prohibited by rabbinic law, one is permitted to walk through the field to show the mourner respect.
דְּאָמַר רַב יְהוּדָה אָמַר שְׁמוּאֵל: מְנַפֵּחַ אָדָם בֵּית הַפְּרָס וְהוֹלֵךְ. וְאָמַר רַב יְהוּדָה בַּר אָשֵׁי מִשְּׁמֵיהּ דְּרַב: בֵּית הַפְּרָס שֶׁנִּדַּשׁ — טָהוֹר.
The Gemara cites proof that the legal status of a beit haperas is unlike the legal status of impurity by Torah law: Rav Yehuda said that Shmuel said: One who passes through a beit haperas may blow on the dust before taking each step, so that if there is a bone beneath the dust, he will expose it, avoid it, and walk. One may not rely on that method of examination with regard to impurity by Torah law. And Rav Yehuda bar Ashi said in the name of Rav: A beit haperas that has been trodden underfoot, creating a path, is pure, and one no longer need be concerned about bones. Clearly, the entire prohibition is a stringency decreed by the Sages.
תָּא שְׁמַע דְּאָמַר רַבִּי אֶלְעָזָר בַּר צָדוֹק: מְדַלְּגִין הָיִינוּ עַל גַּבֵּי אֲרוֹנוֹת שֶׁל מֵתִים, לִקְרַאת מַלְכֵי יִשְׂרָאֵל. וְלֹא לִקְרַאת מַלְכֵי יִשְׂרָאֵל בִּלְבַד אָמְרוּ אֶלָּא אֲפִילּוּ לִקְרַאת מַלְכֵי אוּמּוֹת הָעוֹלָם, שֶׁאִם יִזְכֶּה, יַבְחִין בֵּין מַלְכֵי יִשְׂרָאֵל לְמַלְכֵי אוּמּוֹת הָעוֹלָם. אַמַּאי? לֵימָא ״אֵין חׇכְמָה וְאֵין תְּבוּנָה וְאֵין עֵצָה לְנֶגֶד ה׳״!
The Gemara cites additional proof with regard to the extent to which human dignity overrides mitzvot in the Torah. Come and hear, as Rabbi Elazar bar Tzadok the priest said: I and my fellow priests would jump over coffins of the deceased in order to hurry towards kings of Israel to greet them. And they did not say this only towards kings of Israel, but they said this even towards kings of the nations of the world, so that if one will be privileged to witness the redemption of Israel, he will distinguish between kings of Israel and kings of the nations of the world. The priest violated the Torah prohibition to become ritually impure through contact with the dead, in order to show respect for a king. And why is this? Let us say here too: “There is neither wisdom, nor understanding, nor counsel against the Lord.”
כִּדְרָבָא. דְּאָמַר רָבָא: דְּבַר תּוֹרָה, אֹהֶל, כֹּל שֶׁיֵּשׁ בּוֹ חָלָל טֶפַח — חוֹצֵץ בִּפְנֵי הַטּוּמְאָה. וְשֶׁאֵין בּוֹ חָלָל טֶפַח — אֵינוֹ חוֹצֵץ בִּפְנֵי הַטּוּמְאָה.
The Gemara responds to this challenge by saying that it must be understood in accordance with the opinion of Rava, as Rava said: By Torah law, a tent over a corpse, as long as there is a handbreadth of space between the corpse and the tent over it, constitutes a barrier before the spread of impurity and nothing above the tent can become ritually impure due to impurity imparted by the corpse. And when there is not a handbreadth of space between the corpse and the tent over it, the tent does not constitute a barrier before the spread of impurity and the “pressed” ritual impurity, can reach the heavens.
וְרוֹב אֲרוֹנוֹת יֵשׁ בָּהֶן חָלָל טֶפַח. וְגָזְרוּ עַל שֶׁיֵּשׁ בָּהֶן מִשּׁוּם שֶׁאֵין בָּהֶן. וּמִשּׁוּם כְּבוֹד מְלָכִים לָא גְזַרוּ בְּהוּ רַבָּנַן.
Most coffins have a handbreadth of space. Consequently, their impurity does not spread above the coffin. However, the Sages issued a decree regarding coffins in which there is a handbreadth of space because of those coffins in which there is not. Nevertheless, due to respect for kings, the Sages did not issue a decree in a case involving them and the priests were permitted to jump over the coffins, as it is permitted by Torah law. Therefore, there is no proof from here regarding the question of whether or not human dignity overrides Torah law.
תָּא שְׁמַע: גָּדוֹל כְּבוֹד הַבְּרִיּוֹת שֶׁדּוֹחֶה [אֶת] לֹא תַעֲשֶׂה שֶׁבַּתּוֹרָה.
The Gemara cites an additional proof from a baraita: Come and hear: Great is human dignity, as it overrides a prohibition in the Torah.
וְאַמַּאי? לֵימָא ״אֵין חׇכְמָה וְאֵין תְּבוּנָה וְאֵין עֵצָה לְנֶגֶד ה׳״! תַּרְגְּמַהּ רַב בַּר שְׁבָא קַמֵּיהּ דְּרַב כָּהֲנָא בְּלָאו דְּ״לֹא תָסוּר״. אֲחִיכוּ עֲלֵיהּ, לָאו דְּ״לֹא תָסוּר״ דְאוֹרָיְיתָא הִיא?!
The Gemara asks: Why? Let us also say here: “There is neither wisdom, nor understanding, nor counsel against the Lord.” Rav bar Shaba interpreted this prohibition, which is overridden by human dignity, before Rav Kahana as referring to the prohibition of: “According to the Torah taught to you and the ruling handed down to you, you shall do, you shall not deviate to the left or the right from that which they tell you” (Deuteronomy 17:11). The Yeshiva students laughed at him, as the prohibition of “you shall not deviate” is by Torah law, like all other Torah prohibitions. Why should human dignity override it any more than any other Torah prohibition?
אָמַר רַב כָּהֲנָא: גַּבְרָא רַבָּה אָמַר מִילְּתָא, לָא תְּחִיכוּ עֲלֵיהּ. כׇּל מִילֵּי דְרַבָּנַן אַסְמְכִינְהוּ עַל לָאו דְּ״לֹא תָסוּר״, וּמִשּׁוּם כְּבוֹדוֹ שְׁרוֹ רַבָּנַן.
Rav Kahana replied to them: A great man has spoken, do not laugh at him. The Sages based all rabbinic law on the prohibition of “you shall not deviate”; however, due to concern for human dignity, the Sages permitted suspension of rabbinic law in cases where the two collide. All rabbinic decrees are predicated on the mitzva in the Torah to heed the judges in each generation and to never stray from their words. Therefore, when the Sages suspend a decree in the interest of preserving human dignity, human dignity is overriding a Torah prohibition. In any case, it only overrides rabbinic decrees.
תָּא שְׁמַע: ״וְהִתְעַלַּמְתָּ מֵהֶם״ — פְּעָמִים שֶׁאַתָּה מִתְעַלֵּם מֵהֶם, וּפְעָמִים שֶׁאֵין אַתָּה מִתְעַלֵּם מֵהֶם.
The Gemara cites an additional proof from a baraita: Come and hear: With regard to the laws of returning a lost object, it is stated: “You shall not see the ox of your brother or his sheep go astray and ignore them; return them to your brother” (Deuteronomy 22:1). The baraita explains that the seemingly extraneous expression and disregard them must be understood to give license that at times you disregard lost objects and at times you do not disregard them.
הָא כֵּיצַד? אִם הָיָה כֹּהֵן, וְהִיא בְּבֵית הַקְּבָרוֹת, אוֹ הָיָה זָקֵן וְאֵינָהּ לְפִי כְבוֹדוֹ, אוֹ שֶׁהָיְתָה מְלַאכְתּוֹ מְרוּבָּה מִשֶּׁל חֲבֵרוֹ, לְכָךְ נֶאֱמַר ״וְהִתְעַלַּמְתָּ״. אַמַּאי, לֵימָא ״אֵין חׇכְמָה וְאֵין תְּבוּנָה וְאֵין עֵצָה לְנֶגֶד ה׳״!
How so? If he was a priest and the lost object was in the cemetery, or if he was an elder and it is beneath his dignity to tend to a lost object of that kind, or if he had more work to do than another person and he does not want to set it all aside when another person is available to tend to the lost object. Therefore, with regard to those cases it is stated: And disregard them to permit one to refrain from returning the object. Why? Let us say here, too: Although handling the lost object would be beneath his dignity, “there is neither wisdom, nor understanding, nor counsel against the Lord.”
שָׁאנֵי הָתָם, דִּכְתִיב ״וְהִתְעַלַּמְתָּ מֵהֶם״. וְלִיגְמַר מִינַּהּ? אִיסּוּרָא מִמָּמוֹנָא לָא יָלְפִינַן.
The Gemara answers: There it is different, as it is written: “And disregard them,” indicating that under certain circumstances one is permitted to disregard a lost object. In that case, there is a biblical directive that creates an exception to the prohibition: “You may not disregard” (Deuteronomy 22:3). We found a case in which human dignity overrides a Torah prohibition. The Gemara suggests: Let us derive a general principle that human dignity takes precedence over all mitzvot in the Torah from this case. This possibility is rejected: We do not derive halakhot pertaining to prohibitions from monetary laws, and the case of the lost object merely entails a monetary loss, unlike other prohibitions.
תָּא שְׁמַע.
The Gemara cites an additional proof from a baraita. Come and hear what was said in the Torah with regard to the Nazirite: “He shall not become impure for his father or his mother or his brother or his sister in their death, for the crown of his God is on his head” (Numbers 6:7). Since it was already written with regard to the Nazirite: “He shall not come upon a dead body” (Numbers 6:6), why is it necessary to elaborate and specify his parents and siblings?
״וּלְאַחֹתוֹ״ מַה תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר? הֲרֵי שֶׁהָיָה הוֹלֵךְ לִשְׁחוֹט אֶת פִּסְחוֹ, וְלָמוּל אֶת בְּנוֹ, וְשָׁמַע שֶׁמֵּת לוֹ מֵת, יָכוֹל יַחְזוֹר וְיִטַּמָּא? — אָמַרְתָּ: לֹא יִטַּמָּא.
The Sages derived through halakhic midrash that each of these relationships come to teach a specific nuance of the law. They learned: To what purpose did the verse state: And his sister? To teach that one who was going to slaughter his Paschal lamb and to circumcise his son, both of which are positive mitzvot that if he fails to fulfill them, he is punished with karet, and he heard that a relative of his died, I might have thought that he should return and become ritually impure with the impurity imparted by a corpse. You said: “He shall not become impure”; the death of his relative will not override so significant a mitzva from the Torah.
יָכוֹל: כְּשֵׁם שֶׁאֵינוֹ מִטַּמֵּא לָהֶם כָּךְ אֵינוֹ מִטַּמֵּא לְמֵת מִצְוָה — תַּלְמוּד לוֹמַר ״וּלְאַחוֹתוֹ״ — לַאֲחוֹתוֹ הוּא דְּאֵינוֹ מִטַּמֵּא,
I might have thought: Just as he does not become impure for his relatives, so he does not become impure for a corpse with no one to bury it [met mitzva]. The verse states: “And his sister”; he may not become impure for his sister, as someone else can attend to her burial,